G8BPQ APIs, serial streams, Minicom, TARPN HOST command
The
G8BPQ middleware provides APIs that manifest as virtual /dev serial streams.
Minicom is a terminal emulator that can connect to the
TNC2 API serial stream.
Using
Minicom, a packet network operator can have a textual QSO with another packet network operator.
This QSO is comparable to what's possible in CW or the PSK31 digital mode; however, the packet network is transporting the traffic between the two participants in the QSO.
The TARPN installation script configures Minicom to execute using the com7 serial stream of G8BPQ.
A network operator can access Minicom by launching a terminal session on the Raspberry Pi and entering a tarpn host command.
The operator will then be in the Minicom environment and will have a window for incoming connects from other stations on the network or to create a connection into the network.
Let's try this.
The scripting makes this very easy.
Use
Putty or
Terminal or something similar to open a terminal session into the Raspberry Pi.
Either use SSH from another machine or go to the Raspberry PI desktop and launch Terminal there.
Once you are at the Linux prompt
you can type the command
tarpn host
This will start the
Minicom terminal emulator.
The TARPN version of
Minicom has been modified to do a RING whenever a connection to the host port is made while
Minicom is running, whether the connection is made inbound, or outbound.
The RING is played on the speaker port or the HDMI port (a configuration choice) of the Raspberry Pi, so that you can be notified of a connection even when you are not reading your
Minicom screen.
(Technically, each new connection will will result in the Linux command
aplay being launched with the parameter of
Ring.wav.)
Note that the node software and
Minicom will only allow one connection into and out of the host port at a time.
See also the TARPN TX command for additional outbound connections.
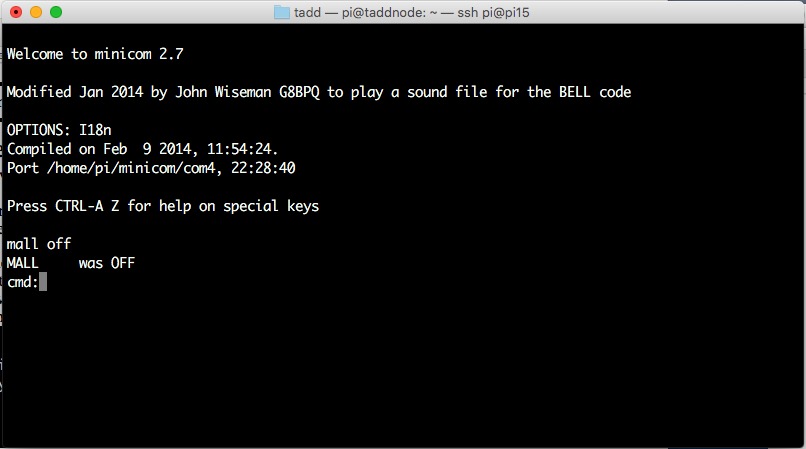
Once
Minicom has started, you are presented with the
cmd: prompt.
The
Minicom terminal is connecting to the
TNC2 API in G8BPQ.
One of the powers of this arrangement between
Minicom and G8BPQ is that you can accept connections from other TARPN nodes.
First I will show you how to do that.
Later on this page I'll give a verbose technical description of all of the commands; the full set of commands will be necessary if you desire to write code to talk to the G8BPQ
TNC2 API.
Using tarpn host to receive incoming connections
When you followed the instructions above, you used
tarpn host to start
Minicom.
You are now presented with a cmd: prompt, and you are ready to receive a connection.
To demonstrate this feature on your own node — a kind of loopback within your node — use
BPQterm or
TARPN-HOME to get into your node and issue the command
host.
This will instruct the node to make a connection to your host-port, which ends up at your
Minicom window.
Here is a screen shot showing my going into
BPQterm and typing
HOST followed by some random text while the
Minicom window is visible.

From the
Minicom you can type a message back to the other window.
To tell
Minicom to disconnect from your incoming caller, send
control-C and type type
d and return.
To exit from
Minicom, send
control A followed by
X and then hit return.
Notice the text saying that Ring.wav was played?
As described above, the sound file is output to the Raspberry PI's audio output jack or HDMI depending on your configuration.
You can replace the Ring.wav file from any of the wav files supplied in the
/home/pi/ringfolder directory.
To select the sound file presto.wav, copy and paste this text into a Linux-prompt terminal window:
mv /home/pi/ringfolder/presto.wav /home/pi/minicom/Ring.wav
and hit return.
To test the soundfile, send this text to the Linux terminal window:
aplay /home/pi/minicom/Ring.wav
Verbose Description
This is a description of
Minicom and the
TNC2 API
Minicom is installed and maintained by the
tarpn start,
tarpn update and
tarpn updateapps scripts.
The application is first installed using the
apt-get package manager and then a modified copy of
Minicom,
called
piminicom is placed in the
/home/pi/minicom directory.
You can send
Minicom a command to quit or change parameters by typing
control-A.
control-A Z will give you help on keys.
If you type text without sending a control-A, you will be sending commands into the
TNC2 API.
At
cmd: you can type one of these commands:
| autolf | Displays or changes the automatic linefeed configuration.
With a parameter of Y or N you may enable or disable automatic linefeed.
|
| bbsmon | Monitor callsigns only -- used to build the JA list in some BBS software?
|
| conok | Displays or changes the connect-OK configuration.
If set to NO then nobody can connect in.
|
| connect | Shows the current CONNECT state.
If you are currently DISCONNECTED, then with a parameter this command will connect to a distant node, a server, or to switch, which represents your own node.
|
| c | Abbreviation for connect.
|
| cr | I don't know what this does. I think it may cause carriage returns to be generated in the outbound (transmit to node) stream when a control-M is received from user application (as if being transmitted to the node).
|
| conv | Needs documentation!.
|
| cpactime | Needs documentation!.
|
| d | tell the API to DISCONNECT.
|
| echo | Displays or changes the local echo configuration.
With a parameter of ON OFF Y or N you may enable or disable local echo.
|
| e | This is the same as echo.
|
| k | leave cmd: and start typing to the node.
|
| mall | Look at or change the state of the Monitor-All feature.
With a parameter of ON OFF Y or N you may enable or disable Monitor-All.
Monitor-All being ON says to include traffic sent unproto or to other stations, instead of just traffic to me, but only if the monitor feature itself is turned on.
See next couple of commands.
It is also unclear to your author if this command does anything at all in the context of a TARPN node.
|
| mcom | Look at or change the state of the Monitor-Comm feature.
With a parameter of ON OFF Y or N you may enable or disable Monitor-Comm.
This feature says that if ON you will see connect, disconnect, acknowledge, and busy packets when you are enabled to watch monitored traffic.
If OFF you will only see Info Frames when you are enabled to watch monitored traffic.
|
| mcon | Look at or change the state of the Monitor-Conn feature.
With a parameter of ON OFF Y or N you may enable or disable Monitor-Conn.
This feature says that if it is ON you will see monitor text even if you are in a connection to the node or to some server.
This can be very confusing.
|
| mc | This is the same as mcon.
|
| monitor | Globally turns on or off monitoring.
|
| mon | Same as monitor.
|
| mtx | Monitor transmit.
|
| mycall | Displays or change the callsign assigned to the serial stream/API.
The callsign appears to be set to the node callsign when the G8BPQ pilinbpq node starts up.
|
| my | This is the same as mycall.
|
| node | This is the same as k.
|
| p | Display the length of packets sent from this terminal.
This command makes you think you can change that length by issuing p and a number.
That features appears to not do anything useful.
|
| sendpac | This may set the character (in hex) used to tell the API that the text typed so far is ready to be sent out as a packet.
|
| trans | Transparent Mode. This tells the TNC2 API to send packets when the buffer is full or a timeout after the first character arrives in the buffer whichever comes first.
I don't know how to specify the rate, yet.
The API will ignore your control characters but will send them into the output stream verbatim.
This is intended for binary file transfer.
To escape from transparent mode, pause for several seconds, then send a control-C, followed by another 2 seconds, followed by another control-C, etc..
It should take 4 control-Cs with pauses to get back to the cmd: prompt
|
| t | Same as trans.
|
| ^C | Get back to cmd:.
Using control-C does not disconnect from the node or network or server. It redirects future traffic to the cmd: processor, stopping it from going into the network or node.
The opposite command is K which tells the API to direct future traffic to the node or network (depending on the state of CONNECT).
|
WB9LOZ, Larry Kenny, has some information on the commands available to a typical TNC. The TNC2 API is attempting to emulate a TNC so Larry's document may be of some use.
Introduction to packet radio part 13
Other G8BPQ APIs
The node software we're using has several different APIs, some of which also use the virtual device driver model.
See the
G8BPQ resources page for more of John Wiseman's (G8BPQ) documentation.
Minicom information
Minicom is installed twice during the
tarpn_install script execution.
The first installation uses
apt-get package manager.
The second installation is the delivery of G8BPQ's
piminicom which gets stored in the
/home/pi/minicom directory.
piminicom is executed from the tarpn script when the command tarpn host is executed from a Linux prompt.
piminicom is launched with this text:
/home/pi/minicom/piminicom -w -D /home/pi/minicom/com7 -S minicom.scr
The file
minicom.scr, which is called out from the launch text, is read by
Minicom and configures the
TNC2 API by sending the text commands contained in the scr file.
This is the contents of that file.
send "^C"
send "D"
send ""
send "autolf on"
send "cbell on"
send "echo on"
send "conok on"
send "mon off"
send "mall off"


 From the Minicom you can type a message back to the other window.
To tell Minicom to disconnect from your incoming caller, send control-C and type type d and return.
To exit from Minicom, send control A followed by X and then hit return.
Notice the text saying that Ring.wav was played?
As described above, the sound file is output to the Raspberry PI's audio output jack or HDMI depending on your configuration.
You can replace the Ring.wav file from any of the wav files supplied in the /home/pi/ringfolder directory.
To select the sound file presto.wav, copy and paste this text into a Linux-prompt terminal window:
From the Minicom you can type a message back to the other window.
To tell Minicom to disconnect from your incoming caller, send control-C and type type d and return.
To exit from Minicom, send control A followed by X and then hit return.
Notice the text saying that Ring.wav was played?
As described above, the sound file is output to the Raspberry PI's audio output jack or HDMI depending on your configuration.
You can replace the Ring.wav file from any of the wav files supplied in the /home/pi/ringfolder directory.
To select the sound file presto.wav, copy and paste this text into a Linux-prompt terminal window: